Robots are increasingly becoming vital assets in the healthcare sector, addressing various challenges that traditional methods struggle to overcome. The integration of robotics in healthcare is enhancing efficiency, improving patient outcomes, and providing support in situations where human resources may be limited. As hospitals face staffing shortages and increased patient loads, robotic solutions offer innovative ways to meet these demands.
With capabilities ranging from surgical assistance to robotic exoskeletons for rehabilitation, these machines are transforming patient care. Their precision and reliability assist medical professionals in performing complex procedures with reduced risk and recovery times. Additionally, robots are being used in elder care, medication delivery, and even providing companionship, showcasing their versatility in enhancing the quality of life for patients.
The adoption of robots in healthcare is not without challenges, including ethical considerations and the need for integration with existing systems. However, the potential for robots to revolutionise healthcare delivery and address pressing issues, such as improving access to care in underserved areas, cannot be overlooked. They represent a significant step towards a more efficient and responsive healthcare system.
The Role of Robotics in Healthcare
Robotics plays a significant role in enhancing healthcare delivery and patient care. From surgical assistance to rehabilitation, these technologies are transforming how medical professionals interact with patients and perform procedures.
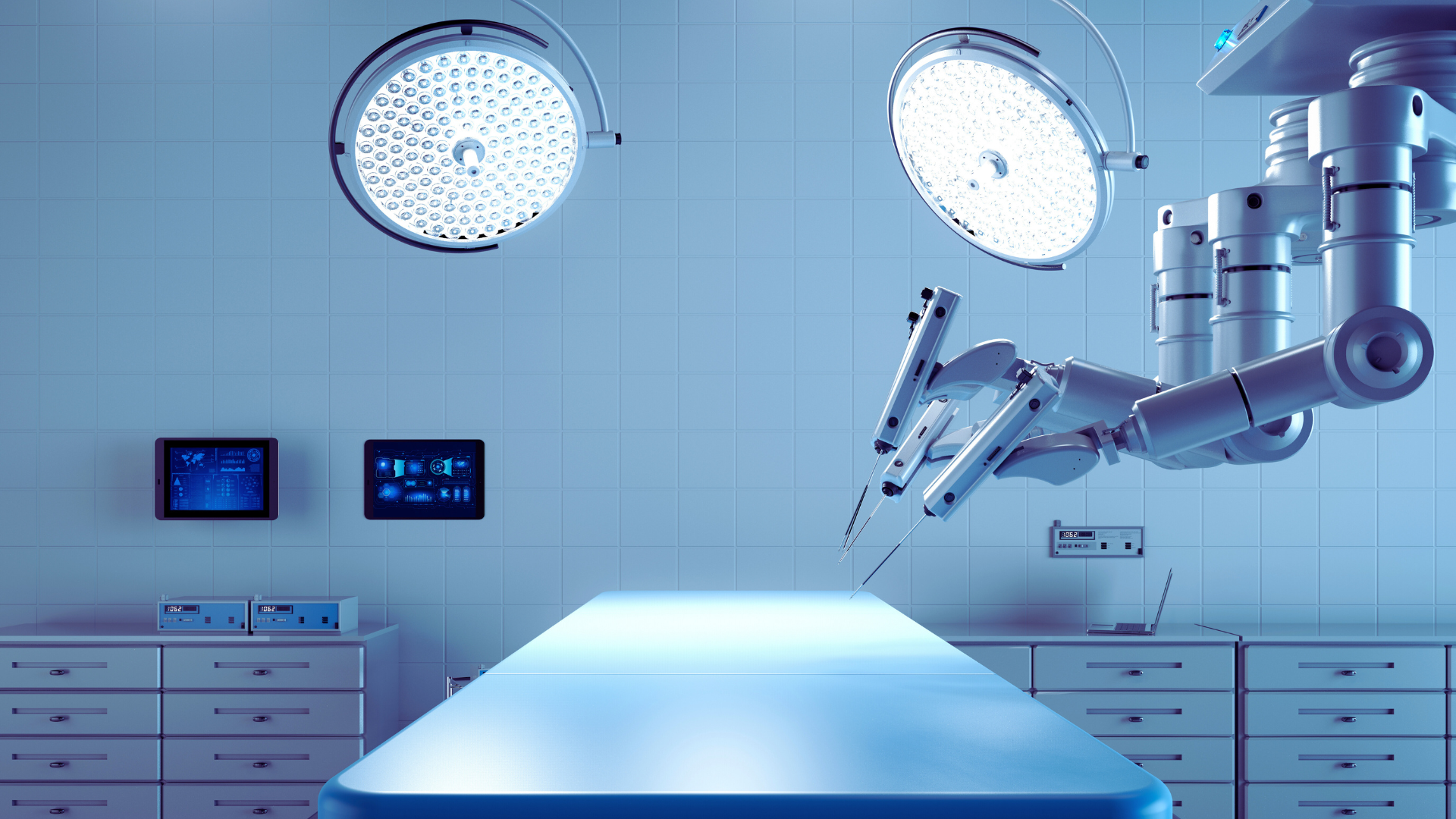
Improving Patient Outcomes with Surgical Robots
Surgical robots have revolutionised operations across various medical specialities. They allow surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with greater precision.
These robots often feature advanced imaging systems and robotic arms that enhance dexterity. Notably, the da Vinci Surgical System has enabled complex surgeries with smaller incisions, resulting in shorter recovery times.
Studies indicate that procedures conducted with robotic assistance can lead to reduced complications and improved patient outcomes. The integration of robotics in surgery demonstrates a trend towards greater efficiency and effectiveness in patient care.
Telepresence Robots: Bridging the Healthcare Gap
Telepresence robots enhance access to medical care, particularly in remote or underserved areas. These robots enable healthcare providers to interact with patients through video conferencing technology.
They provide a vital link for consultations, monitoring, and even remote diagnostics. Patients benefit from the ability to receive care without the need for lengthy travel.
Many healthcare facilities have adopted telepresence robots to ensure continuous patient support, especially during crises. Their role is crucial in maintaining communication between healthcare providers and patients.
Rehabilitation Robots and Quality of Life
Rehabilitation robots offer valuable support for patients recovering from injuries or surgeries. These devices assist in mobility training and physical therapy, promoting independence and enhancing quality of life.
Robotics in rehabilitation may involve exoskeletons or robotic limbs designed to help patients regain movement. Research shows that these interventions can accelerate recovery by providing consistent and adaptive support during therapy.
Integrating robotics into rehabilitation programmes also allows healthcare professionals to personalise treatment regimens effectively. This focus on tailored care can significantly improve rehabilitation outcomes for patients.
Overcoming Healthcare Challenges
Robots are transforming healthcare by addressing various challenges. These advancements range from managing pandemics to improving elderly care and ensuring the accurate administration of medication.
Tackling the COVID-19 Pandemic with Robotics
During the COVID-19 pandemic, robots played a crucial role in infection control and patient management. They assisted in the disinfection of hospital environments, which helped reduce healthcare-associated infections.
Delivery robots transported supplies and medications, minimising human contact and curbing the spread of the virus. Additionally, robots were employed for remote patient monitoring, allowing healthcare professionals to check on patients while maintaining social distancing.
Assisted Care for the Ageing Population
As the global population ages, the demand for elderly care is increasing. Robots have become essential in providing support for the elderly, assisting with daily tasks such as medication reminders, mobility assistance, and social interaction.
Assistive robots promote independence and enhance the quality of life for seniors. They enable caregivers to focus on more complex tasks while ensuring that the elderly receive timely support, thus alleviating pressure on healthcare systems.
Robots Ensuring Precise Drug Administration
Robotic systems are improving the accuracy of drug administration in hospitals. Inpatient pharmacies employ robotic technology to prepare and dispense medications, reducing human error.
These robots ensure that the correct dosages are packaged and delivered to patients, enhancing patient safety. Furthermore, they streamline the medication delivery process, allowing healthcare providers to allocate more time to patient care.
Ethical and Logistical Considerations
The integration of robots in healthcare raises important ethical and logistical issues that must be addressed. Considerations around privacy, accountability, and human connection are critical to ensure the successful adoption of robotic technologies in medical settings.
Privacy and Security in Robotic Healthcare
Robotic systems often handle sensitive patient data, raising privacy and security concerns. Systems must adhere to strict regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which mandates data protection principles.
Concerns arise regarding data breaches and unauthorised access. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures is essential for protecting patient information. For instance, encryption techniques and secure multi-layer authentication can significantly mitigate risks.
Furthermore, human-robot interaction requires transparency in data usage. Patients must understand how their data is collected, stored, and utilised. Clear communication enhances public trust and acceptance of robotic technologies in the healthcare sphere.
Accountability and Trust in Machine Learning
The rise of machine learning in robotic healthcare necessitates clear lines of accountability. Questions about who is responsible for a robot’s actions are paramount. Providers must outline responsibilities when machines make diagnostic or treatment decisions.
Trust in these systems is founded on their reliability and accuracy. A transparent process for algorithm development and validation can foster public confidence. Demonstrating the effectiveness of these technologies through rigorous clinical trials can further solidify this trust.
Additionally, ethical implications arise from automated decision-making. Ensuring human oversight helps maintain autonomy in patient care and prevents potential biases in machine learning algorithms.
Maintaining Human Connection in Healthcare
The introduction of robots in healthcare must not undermine the essential human connection between patients and caregivers. Empathy and compassion are fundamental to effective healthcare delivery.
Robots can augment healthcare services by performing routine tasks, thus allowing healthcare professionals to devote more time to personal interactions. However, the use of robots should enhance rather than replace human engagement.
Public acceptance may hinge on how well technology integrates with human roles. Promoting a balance between robotic efficiency and human compassion is key to successful implementation, ensuring that technology supports—not supplants—the vital human touch in patient care.
Technological Advancements and Future Prospects
Recent technological advancements in healthcare are shaping innovative strategies for improving patient outcomes. The emergence of artificial intelligence, virtual reality, and robotics is transforming operations and enhancing the quality of care in clinical settings.
Incorporating AI and VR into Clinical Practice
Artificial intelligence is streamlining diagnostics through advanced data analytics. By analysing large datasets, AI algorithms can identify patterns and predict health outcomes more accurately than traditional methods.
Virtual reality is redefining training processes for healthcare professionals. It provides immersive simulations that enhance the learning experience. This technology allows practitioners to gain hands-on experience without risking patient safety.
Combining AI and VR offers significant potential for remote consultations as well. AI-driven chatbots and virtual therapists can address patient queries promptly, improving access to care.
The Growing Trend of Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, are being integrated into surgical environments. They assist surgeons by providing precision and stability during complex procedures. Their ability to work alongside humans promotes operational efficiency and reduces errors.
Additionally, cobots are now aiding in routine tasks, such as dispensing medication and managing inventories. This alleviates the workload on healthcare staff, allowing them to focus on more critical activities.
Data analytics also play a role in optimising cobot performance by identifying workflow bottlenecks and enhancing productivity metrics.
Autonomous Systems and Operational Efficiency
Autonomous systems are revolutionising logistics within healthcare facilities. These robots can autonomously transport supplies, medications, and even samples, ensuring timely deliveries.
The implementation of these systems significantly enhances operational efficiency. By reducing human involvement in monotonous tasks, healthcare providers can allocate resources more effectively.
Moreover, autonomous systems contribute to accuracy in medication administration. They decrease the chances of human error, which can lead to adverse patient outcomes. The future holds promise for the continued integration of these technologies, facilitating safer and more efficient healthcare environments.

Leave a Reply